Executive Summary
Becoming a data scientist involves a combination of education, technical skills, hands-on experience, and continuous learning. As one of the most sought-after roles in today’s data-driven economy, data scientists transform raw data into actionable insights that drive business decisions. This guide provides a step-by-step roadmap to becoming a data scientist, including the skills, tools, education, and practical experience required to succeed in this dynamic field.
Table of Content
Step 1: Understand the Role of a Data Scientist
Before pursuing a career, it is essential to understand what data scientists do:
- Analyze large datasets to identify patterns and trends.
- Build predictive and prescriptive models using statistical and machine learning techniques.
- Communicate insights to stakeholders through reports, dashboards, and visualizations.
- Support strategic decision-making and solve complex business problems.
Knowing the scope of the role helps in identifying the skills and qualifications needed.
Step 2: Obtain the Necessary Education
Most data scientist roles require a solid foundation in mathematics, statistics, and computer science:
- Undergraduate Degree:
- Fields: Computer Science, Statistics, Mathematics, Engineering, or related disciplines.
- Focus on courses in data structures, algorithms, probability, and linear algebra.
- Advanced Degrees (Optional but Beneficial):
- Master’s or PhD in Data Science, AI, Machine Learning, or Business Analytics.
- Provides deeper knowledge and better career opportunities, especially in research or advanced analytics roles.
- Online Courses & Certifications:
- Platforms like Coursera, Udemy, EdX, and DataCamp offer specialized data science programs.
- Certificates in Python, R, SQL, machine learning, or AI can boost employability.
Step 3: Learn Key Skills
A data scientist must master a mix of technical and analytical skills:

Technical Skills:
- Programming: Python, R, SQL.
- Data Manipulation: Pandas, NumPy, Excel.
- Machine Learning & AI: Scikit-learn, TensorFlow, PyTorch.
- Data Visualization: Matplotlib, Seaborn, Tableau, Power BI.
- Big Data Tools: Hadoop, Spark, AWS, Azure.
Analytical Skills:
- Statistical analysis and hypothesis testing.
- Predictive modeling and regression analysis.
- Problem-solving and critical thinking.
Soft Skills:
- Effective communication of technical findings.
- Collaboration with cross-functional teams.
- Domain knowledge relevant to the industry (finance, healthcare, marketing, etc.).
If you’re ready to dive deeper into the data field, there are several career paths to explore.
- Begin with How to Become a Data Scientist: The Complete Step-by-Step Roadmap — a comprehensive guide that outlines specific learning milestones, tools, and portfolio strategies.
- For those curious about the engineering side of data systems, explore What Does a Data Engineer Do? Roles, Skills, and Career Path Explained.
- And if you’re considering research or academia to deepen your expertise, check out What Does PhD Stand For? An In-Depth Guide to the Doctor of Philosophy Degree.
Step 4: Gain Practical Experience
Hands-on experience is crucial for becoming job-ready:
- Projects and Portfolio:
- Work on datasets to analyze trends, build models, and visualize results.
- Showcase projects on GitHub or personal websites to demonstrate skills.
- Internships:
- Apply for internships in tech companies, startups, or research labs.
- Gain exposure to real-world business problems and datasets.
- Kaggle Competitions & Hackathons:
- Participate in challenges to solve real-world problems.
- Learn from the community and build a strong professional network.
Step 5: Build a Professional Network
Networking helps in learning, mentorship, and job opportunities:
- Join data science communities and forums (Kaggle, Reddit, LinkedIn groups).
- Attend workshops, webinars, and conferences.
- Connect with professionals and recruiters in the industry.
Step 6: Apply for Entry-Level Data Science Roles
Once you have the necessary skills and experience, you can pursue roles such as:
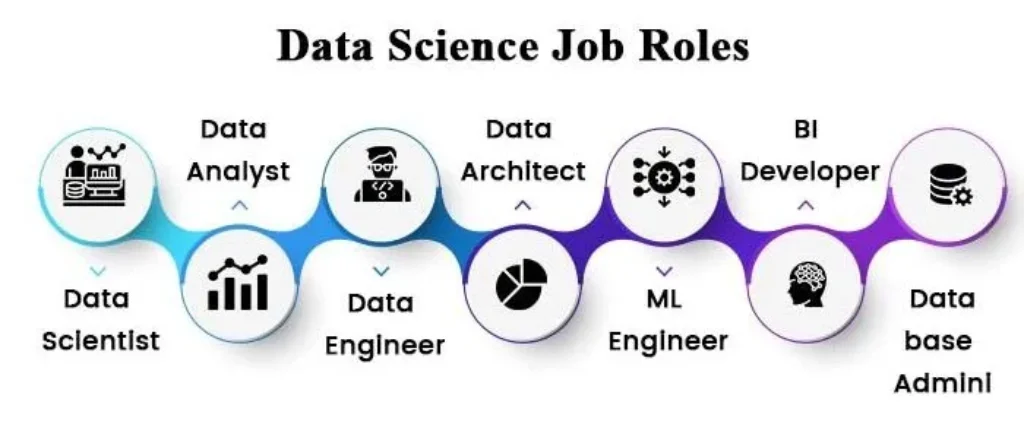
- Data Analyst → Transition to Data Scientist.
- Junior Data Scientist.
- Machine Learning Engineer (for technically oriented roles).
Prepare a strong resume highlighting:
- Projects demonstrating data analysis and modeling.
- Programming proficiency.
- Any relevant certifications or online courses.
Step 7: Continuous Learning and Specialization
Data science is a rapidly evolving field. Continuous learning is essential:
- Stay updated with new tools, algorithms, and best practices.
- Consider specialization areas such as:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Computer Vision
- Predictive Analytics
- Big Data Engineering
- Take advanced certifications or online courses to stay competitive.
Conclusion
Becoming a data scientist requires a combination of education, technical expertise, practical experience, and continuous learning. By following a structured path—from understanding the role, acquiring relevant skills, gaining hands-on experience, building a portfolio, to networking and specializing—aspiring professionals can establish a successful and rewarding career in data science.


