Executive Summary
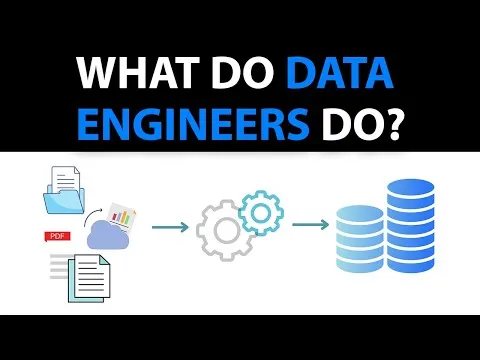
A data engineer is a technology professional who designs, builds, and maintains the infrastructure and systems that enable organizations to collect, store, and analyze large volumes of data efficiently. While data scientists focus on interpreting and analyzing data, data engineers create the pipelines and architectures that make this data accessible, reliable, and usable.
This guide explores the role of a data engineer, core responsibilities, required skills, tools and technologies, career prospects, and how data engineers contribute to modern data-driven organizations.
Table of Content
Understanding the Role of a Data Engineer
1.1 Definition
A data engineer is responsible for designing and managing the systems and architecture that collect, process, and store data from multiple sources. They ensure that data is clean, structured, and readily available for analysis or operational use.
1.2 Importance of Data Engineering
Data engineering forms the backbone of data-driven decision-making. Without efficient data pipelines and storage solutions, data scientists and analysts would struggle to access reliable information. Data engineers:
- Build scalable systems for handling large datasets.
- Ensure data is accurate, consistent, and timely.
- Enable organizations to make data-driven decisions quickly.
- Optimize the performance of data workflows and systems.
Core Responsibilities of a Data Engineer
- Designing Data Architecture
- Create data models and database structures.
- Plan data warehouses, lakes, and pipelines for optimal performance.
- Building and Maintaining Data Pipelines
- Extract, transform, and load (ETL) processes from various sources.
- Automate workflows to ensure continuous data flow.
- Data Integration
- Consolidate data from different systems, databases, and third-party sources.
- Ensure compatibility and consistency across data platforms.
- Data Quality and Governance
- Implement validation, cleaning, and transformation procedures.
- Ensure compliance with data privacy and security standards.
- Collaboration
- Work with data scientists, analysts, and business teams to understand requirements.
- Translate business needs into technical solutions and infrastructure.
- Performance Optimization
- Monitor system performance and optimize queries, storage, and pipelines.
- Scale data systems to handle increasing data volumes efficiently.
Key Skills Required
Data engineers need a strong mix of technical, analytical, and problem-solving skills:
Technical Skills
- Programming: Python, Java, Scala, or SQL
- Database Management: MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, Oracle
- Big Data Technologies: Hadoop, Spark, Kafka
- ETL Tools: Talend, Informatica, Apache Airflow
- Cloud Platforms: AWS, Azure, Google Cloud Platform
Analytical Skills
- Understanding of data modeling and relational databases
- Knowledge of data warehousing, pipelines, and architecture
- Problem-solving for data flow optimization and system scalability
Soft Skills
- Collaboration and communication across technical and business teams
- Attention to detail and quality assurance
- Project management and documentation skills
Data engineering often works hand in hand with other data-focused roles and disciplines.
- To understand how to transition into analytical roles or expand your skill set, explore How to Become a Data Scientist: The Complete Step-by-Step Roadmap.
- If you’re just starting out and want to build a structured learning plan, check out How to Start a Career in Data Science: Education, Skills & Experience Explained.
- And for professionals considering advanced academic routes in machine learning or AI research, What Does PhD Stand For? An In-Depth Guide to the Doctor of Philosophy Degree explains how doctoral studies can enhance your career in data and innovation.
Tools and Technologies
| Category | Tools & Platforms |
|---|---|
| Programming | Python, Java, Scala, SQL |
| Databases | MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, Oracle |
| ETL & Pipelines | Apache Airflow, Talend, Informatica |
| Big Data | Hadoop, Spark, Kafka, Hive |
| Cloud | AWS, Google Cloud, Azure |
| Version Control | Git, GitHub, GitLab |
Career Outlook
The demand for data engineers has grown significantly as organizations process increasing volumes of data.
- Salary Potential: Entry-level data engineers earn $70,000–$90,000 per year; experienced engineers can earn $120,000–$160,000 or more.
- Career Growth: Opportunities to advance into senior engineering roles, solutions architecture, or data platform management.
- Global Demand: Companies across finance, healthcare, tech, e-commerce, and government sectors require data engineering expertise.
How Data Engineers Differ from Data Scientists
| Aspect | Data Engineer | Data Scientist |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Infrastructure, pipelines, and storage | Analysis, modeling, insights |
| Tools | SQL, ETL tools, big data platforms | Python, R, ML frameworks |
| Goal | Reliable, accessible data | Decision-making, predictions |
| Key Skills | Programming, database design, cloud | Statistics, ML, data visualization |
Benefits of Hiring a Data Engineer
- Ensures data reliability and accessibility for analytics teams
- Supports scalable and efficient data architectures
- Reduces operational bottlenecks in data processing
- Enhances data quality and governance, ensuring compliance
- Enables faster, data-driven decision-making
Challenges Faced by Data Engineers
- Managing large-scale and complex datasets
- Integrating data from diverse sources and formats
- Maintaining system performance and scalability
- Ensuring data privacy and compliance with regulations
- Keeping up with rapidly evolving technologies and platforms
Pathway to Becoming a Data Engineer
- Educational Background
- Undergraduate degree in Computer Science, Software Engineering, IT, or related fields
- Courses in databases, programming, and systems architecture
- Key Skills Development
- Programming: Python, Java, Scala
- SQL and database management
- Big data tools and cloud platforms
- Practical Experience
- Internships and projects involving ETL, pipelines, or cloud infrastructure
- Contribution to open-source projects and data platform development
- Certifications
- Cloud certifications: AWS Certified Data Analytics, Google Cloud Professional Data Engineer
- Big Data: Cloudera, Hortonworks, or Databricks certifications
- ETL and pipeline tools: Apache Airflow or Informatica
- Portfolio Development
- Showcase projects involving pipelines, data warehousing, or big data processing
- Demonstrate problem-solving and optimization of data workflows
- Job Search
- Apply for roles like Junior Data Engineer, ETL Developer, Big Data Engineer
- Highlight technical skills, certifications, and project experience
Career Growth and Specializations
- Senior Data Engineer: Lead data architecture and pipelines
- Big Data Engineer: Focus on high-volume distributed systems
- Cloud Data Engineer: Specialize in cloud data platforms and solutions
- Data Platform Manager: Oversee enterprise-wide data infrastructure
- Data Solutions Architect: Design and implement comprehensive data systems
Conclusion
A data engineer is a critical player in modern data ecosystems, providing the infrastructure and systems that enable data scientists, analysts, and organizations to extract maximum value from their data. With strong programming skills, knowledge of databases, ETL processes, and cloud platforms, data engineers ensure data is reliable, scalable, and actionable. This role offers strong career prospects, opportunities for specialization, and the chance to work at the forefront of the data revolution.


