
Executive Summary
Business management is the strategic process of planning, organizing, directing, and controlling the resources, operations, and activities of an organization to achieve its objectives efficiently and effectively.
It is a multidimensional field encompassing leadership, strategic planning, finance, human resources, marketing, operations, and risk management.
Effective business management enables organizations to maximize productivity, profitability, and sustainability while maintaining a competitive edge in the market. It integrates people, processes, and technology to deliver optimal outcomes.
This comprehensive guide explores what business management is, its core principles, functions, strategies, benefits, challenges, and emerging trends, offering insights for students, professionals, and business leaders.
Table of Content
Introduction
In today’s fast-paced global economy, organizations of all sizes face unprecedented challenges and opportunities. From small startups to multinational corporations, every business relies on management practices to operate efficiently and stay competitive.
Business management is the framework that aligns resources, processes, and personnel to achieve strategic objectives while adapting to changing market conditions.
At its core, business management is about making informed decisions, optimizing operations, and fostering a productive and innovative work culture. Managers play a pivotal role in shaping organizational direction, coordinating teams, and ensuring that objectives are met.
The Meaning and Scope of Business Management
Business management is more than simply overseeing daily operations; it is a holistic approach that encompasses:
- Strategic Planning – Setting long-term goals and determining the best approach to achieve them.
- Resource Allocation – Efficiently using human, financial, and material resources.
- Operational Oversight – Ensuring that processes, systems, and workflows are effective.
- Leadership and People Management – Motivating employees and cultivating a positive organizational culture.
- Financial Management – Planning budgets, managing cash flows, and controlling costs.
- Marketing and Sales Management – Developing strategies to attract and retain customers.
- Risk Management – Identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential threats to the business.
The scope of business management varies across industries, but its core objective remains consistent: achieving organizational goals efficiently while ensuring sustainability and growth.
Core Principles of Business Management
Several foundational principles guide effective business management:
- Planning – Establishing objectives, anticipating challenges, and devising strategies to achieve goals.
- Organizing – Structuring teams, delegating responsibilities, and allocating resources effectively.
- Leading – Inspiring, guiding, and motivating employees to achieve organizational goals.
- Controlling – Monitoring performance, comparing results against objectives, and implementing corrective actions.
- Decision-Making – Analyzing data, weighing options, and making informed choices.
- Efficiency and Productivity – Maximizing output while minimizing waste of time, resources, and effort.
- Adaptability – Responding to changes in market conditions, technology, and customer preferences.
These principles ensure that managers can balance strategic vision with operational effectiveness, delivering tangible results.
Boost Your Business Management Skills
Take your understanding of business management further with these top-rated online courses designed to enhance your strategic, financial, and leadership expertise:
- Business Strategy – Master how to plan and execute winning strategies that drive growth.
- Cybersecurity for Business Specialization – Learn to protect your organization’s data and manage digital risks effectively.
- Business Finance and Data Analysis Fundamentals – Build financial acumen and make data-driven management decisions.
- Business Value and Project Management Specialization – Gain project leadership skills to deliver measurable results.
- Business Data Management and Communication Specialization – Strengthen your data storytelling and business communication skills.
Choose a course that aligns with your goals and start advancing your business career today.
Functions of Business Management
Business management is broadly categorized into several interrelated functions:
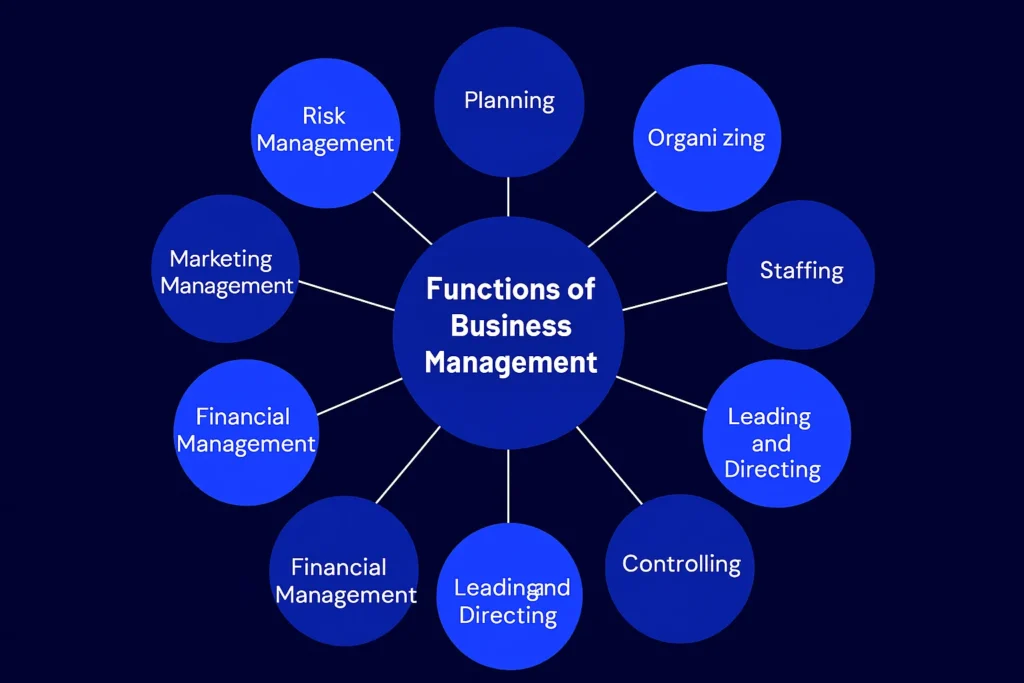
1. Planning
- Establishing short-term and long-term goals.
- Identifying resources, risks, and opportunities.
- Developing business strategies, operational plans, and contingency plans.
2. Organizing
- Designing organizational structure and reporting hierarchies.
- Assigning roles and responsibilities.
- Coordinating tasks and resources to achieve goals efficiently.
3. Staffing
- Recruiting, hiring, and onboarding employees.
- Training and developing workforce skills.
- Ensuring appropriate staffing levels for operational needs.
4. Leading and Directing
- Motivating employees and encouraging collaboration.
- Fostering innovation, creativity, and problem-solving.
- Communicating vision, expectations, and objectives clearly.
5. Controlling
- Monitoring operational performance against established benchmarks.
- Evaluating efficiency, quality, and profitability.
- Implementing corrective measures to address gaps or inefficiencies.
6. Financial Management
- Budgeting, accounting, and financial reporting.
- Managing investments, expenses, and revenue streams.
- Analyzing financial performance to guide strategic decisions.
7. Marketing and Sales Management
- Conducting market research and identifying target audiences.
- Developing marketing campaigns, branding, and promotional strategies.
- Managing customer relationships, sales pipelines, and revenue growth.
8. Risk Management
- Identifying potential internal and external threats.
- Assessing likelihood and impact of risks.
- Implementing mitigation strategies to minimize losses.
Understanding business management connects with several other key areas of organizational success.
If you’re interested in how business operations, people, and performance come together, these guides offer deeper insights:
- What Is Operations Management? – Learn how organizations optimize processes and resources to achieve efficiency.
- What Is Human Capital Management (HCM)? – Explore how managing people strategically strengthens business performance.
- What Is Performance Management? – Discover how companies evaluate and enhance employee performance to meet business goals.
- What Is Time Management? – Understand how effective time management directly impacts leadership and productivity.
- What Is Knowledge Management? – See how sharing and managing information drives smarter decision-making in business.
Key Areas of Business Management
Business management covers multiple functional areas that collectively ensure organizational success:
- Operations Management – Optimizing production processes and workflow efficiency.
- Human Resource Management – Recruiting, developing, and retaining talent.
- Financial Management – Controlling costs, budgeting, and ensuring profitability.
- Marketing Management – Building customer relationships and driving sales growth.
- Strategic Management – Formulating long-term plans and achieving competitive advantage.
- Information Technology Management – Leveraging technology to improve operations and decision-making.
- Supply Chain Management – Coordinating procurement, production, and distribution.
- Customer Relationship Management – Maintaining loyalty and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Business Management Strategies
Successful businesses adopt strategies to maintain efficiency, growth, and competitiveness:
- Strategic Planning – Developing long-term vision and objectives.
- Lean Management – Reducing waste while increasing efficiency and value.
- Agile Management – Adapting quickly to changes in market demand or technology.
- Six Sigma and Quality Control – Ensuring high-quality products and services.
- Innovation Management – Encouraging creativity and implementing new ideas.
- Performance-Based Management – Linking incentives to employee and organizational outcomes.
- Global Expansion Strategies – Entering new markets and diversifying business operations.
- Sustainability Initiatives – Integrating environmentally responsible practices.
Tools and Technologies in Business Management
Modern business management relies on technology to streamline processes, analyze data, and optimize decision-making:
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): SAP, Oracle NetSuite, Microsoft Dynamics
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Salesforce, HubSpot, Zoho CRM
- Project Management Tools: Asana, Trello, Monday.com, Wrike
- Financial Management Software: QuickBooks, Xero, FreshBooks
- Business Intelligence and Analytics: Tableau, Power BI, Google Data Studio
- Collaboration Platforms: Microsoft Teams, Slack, Google Workspace
- HR Management Systems: Workday, BambooHR, ADP Workforce
Benefits of Business Management
Proper business management delivers numerous benefits to organizations:
- Increased Productivity – Efficient workflows and optimized resource use enhance output.
- Cost Efficiency – Effective planning reduces waste and operational costs.
- Improved Decision-Making – Data-driven strategies help in making informed choices.
- Employee Engagement – Strong leadership and communication foster motivation and retention.
- Customer Satisfaction – Organized operations and quality control ensure better products and services.
- Risk Mitigation – Anticipating challenges reduces the likelihood of business failures.
- Competitive Advantage – Strategic management keeps the business ahead of rivals.
- Sustainable Growth – Long-term planning ensures profitability and market stability.
Challenges in Business Management
Despite its benefits, business management faces multiple challenges:

- Economic Volatility – Market fluctuations affect operations and profitability.
- Technological Change – Rapid advancements require continual adaptation.
- Global Competition – Businesses must compete on quality, cost, and innovation.
- Workforce Management – Attracting, developing, and retaining talent is complex.
- Regulatory Compliance – Adhering to legal and environmental standards is critical.
- Customer Expectations – Meeting changing preferences requires agility.
- Resource Constraints – Limited capital, manpower, or materials can hinder growth.
Emerging Trends in Business Management
Business management is evolving to meet modern challenges and opportunities:
- Digital Transformation – Leveraging AI, machine learning, and cloud computing.
- Sustainable Business Practices – Integrating eco-friendly strategies into operations.
- Remote and Hybrid Work Models – Managing distributed teams effectively.
- Data-Driven Decision Making – Using analytics for operational and strategic insight.
- Agile and Lean Practices – Enhancing flexibility, responsiveness, and efficiency.
- Globalization – Expanding into international markets while managing cultural diversity.
- Customer-Centric Strategies – Placing customer experience at the heart of operations.
- Innovation and Entrepreneurship – Encouraging creative solutions and business model innovation.
Real-World Applications
- Startups – Using management practices to establish processes, attract funding, and scale operations.
- Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) – Improving efficiency and competitive positioning.
- Large Corporations – Coordinating complex operations across multiple divisions and regions.
- Retail and E-Commerce – Managing supply chains, inventory, and customer engagement.
- Healthcare – Streamlining hospital operations, patient care, and administrative workflows.
- Manufacturing – Optimizing production lines, quality control, and logistics.
- Service Industries – Enhancing client satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Common Misconceptions
- Business Management is Only for CEOs or Executives – It applies to managers at all levels.
- It’s Only About Making Profits – Business management balances profitability with sustainability, ethics, and employee satisfaction.
- Technology Can Replace Management – Tools assist, but leadership, strategy, and human judgment are essential.
- Planning Alone is Sufficient – Execution, monitoring, and adjustment are equally important.
Key Metrics and KPIs
Measuring the effectiveness of business management is critical:
- Revenue Growth – Year-over-year increase in sales.
- Profit Margins – Net income as a percentage of revenue.
- Employee Productivity – Output per employee or per department.
- Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT) – Quality of service or product perception.
- Operational Efficiency – Cost per unit, cycle time, or workflow effectiveness.
- Market Share – Organization’s share in its industry.
- Employee Retention Rate – Percentage of employees retained over a period.
- Return on Investment (ROI) – Evaluating profitability of investments.
Conclusion
Business management is the art and science of coordinating people, processes, and resources to achieve organizational goals. It is a dynamic, multifaceted discipline that spans planning, leadership, operations, finance, marketing, and strategic decision-making.
By implementing effective management practices, organizations can increase efficiency, reduce costs, mitigate risks, and ensure sustainable growth. In a rapidly changing business environment, understanding and applying business management principles is essential for anyone seeking to lead, grow, or participate in a successful enterprise.


