Executive Summary
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is a strategic approach that businesses use to manage interactions with current and potential customers. It involves the use of technology, processes, and practices to organize, automate, and synchronize sales, marketing, customer service, and support. CRM systems enable companies to understand customer behavior, enhance engagement, improve retention, and ultimately increase revenue.
In a competitive business environment, CRM is critical for building long-term relationships, providing personalized experiences, and leveraging data to make informed decisions. This guide explores CRM’s definition, history, components, types, processes, benefits, challenges, tools, best practices, and real-world applications to provide a complete understanding of its strategic importance.
Table of Content
Introduction
Customer relationships are at the heart of any successful business. Companies that maintain strong relationships with their customers can foster loyalty, drive repeat business, and generate positive word-of-mouth. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is a structured approach to managing these relationships effectively.
CRM is not just software; it is a business philosophy and strategy designed to enhance interactions, anticipate customer needs, and deliver personalized experiences. By integrating people, processes, and technology, CRM helps organizations understand their customers better and respond proactively to their requirements.
History and Evolution of CRM
The concept of CRM has evolved significantly over the decades:
- Manual Systems (1950s–1970s) – Customer information was recorded manually in ledgers, index cards, and filing systems. Businesses relied on direct interaction and personal memory to maintain relationships.
- Database Marketing (1980s) – Companies began using relational databases to store customer information. Marketing campaigns were targeted based on customer data, enhancing efficiency.
- Early CRM Software (1990s) – Software solutions emerged to manage customer data, track interactions, and support sales teams.
- Cloud-Based CRM (2000s) – SaaS (Software as a Service) models allowed businesses of all sizes to access CRM tools without heavy infrastructure costs.
- AI and Advanced Analytics (2010s–Present) – Modern CRM platforms integrate artificial intelligence, predictive analytics, and automation to deliver personalized customer experiences and optimize business processes.
Definition of Customer Relationship Management
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is the strategic practice of managing a company’s interactions with current and potential customers. It uses data, technology, and processes to:
- Centralize customer information
- Track interactions across multiple channels
- Automate sales, marketing, and service processes
- Analyze customer behavior and preferences
- Improve engagement, retention, and loyalty
CRM is both a business philosophy and a technology solution that enables organizations to deliver exceptional customer experiences and foster long-term relationships.
Core Components of CRM
A comprehensive CRM system integrates multiple components to manage the entire customer lifecycle:
- Sales Force Automation (SFA) – Automates the sales process, tracks leads, opportunities, and deals, and provides visibility into the sales pipeline.
- Marketing Automation – Manages campaigns, segment audiences, track engagement, and measure campaign performance to attract and retain customers.
- Customer Service and Support – Tracks customer issues, facilitates ticket management, provides self-service portals, and ensures timely resolution.
- Analytics and Reporting – Collects data across touchpoints to analyze customer behavior, preferences, and trends for informed decision-making.
- Collaboration Tools – Facilitates communication across teams and departments, ensuring everyone has access to up-to-date customer information.
- Integration Capabilities – Connects CRM systems with other business tools such as ERP, e-commerce platforms, and social media to provide a 360-degree view of the customer.
Recommended Courses to Strengthen Your CRM Skills
Take your customer relationship skills to the next level with these powerful learning options:
- IBM: Developing Interpersonal Skills – Learn how to communicate effectively, build trust, and manage relationships that lead to customer loyalty.
- Google: From Likes to Leads – Interact with Customers Online – Master the art of online engagement, turning social interactions into meaningful business relationships.
Perfect for anyone looking to boost both personal and digital customer-management skills.
Types of CRM
CRM systems can be categorized based on their focus and functionality:

1. Operational CRM
- Focuses on automating and improving customer-facing processes, including sales, marketing, and service.
- Helps streamline workflows and ensure consistent customer interactions.
2. Analytical CRM
- Focuses on analyzing customer data to uncover insights about behavior, preferences, and trends.
- Supports strategic decision-making, targeting, and personalization.
3. Collaborative CRM
- Emphasizes sharing customer information across departments, including sales, marketing, and service.
- Enhances communication and coordination to deliver consistent customer experiences.
4. Strategic CRM
- Focuses on long-term customer engagement and loyalty strategies.
- Aligns business objectives with customer needs and expectations.
Key Processes in CRM
CRM is implemented through structured processes that manage the entire customer lifecycle:
1. Lead Management
- Capturing, tracking, and qualifying potential customers.
- Prioritizing leads based on likelihood to convert.
2. Contact Management
- Centralizing customer information including demographics, interaction history, preferences, and communications.
3. Opportunity Management
- Tracking potential sales opportunities and monitoring their progress through the sales pipeline.
4. Customer Service Management
- Handling customer queries, complaints, and support requests efficiently.
- Ensuring timely resolution and customer satisfaction.
5. Marketing Management
- Planning and executing targeted campaigns.
- Segmenting audiences, automating workflows, and measuring engagement.
6. Analytics and Insights
- Collecting and analyzing data from multiple channels.
- Identifying trends, predicting customer behavior, and personalizing interactions.
Benefits of CRM
CRM delivers significant benefits to businesses and customers alike:
1. Enhanced Customer Relationships
- Personalized experiences and proactive communication strengthen loyalty and trust.
2. Increased Sales Efficiency
- Automates repetitive tasks, tracks opportunities, and improves sales pipeline visibility.
3. Improved Customer Retention
- Timely support, follow-ups, and targeted engagement increase customer satisfaction and reduce churn.
4. Data-Driven Decision Making
- Provides actionable insights for marketing, sales, and service strategies.
5. Streamlined Processes
- Automates workflows across departments, reducing errors and inefficiencies.
6. Better Collaboration
- Teams share customer data and insights, enhancing internal coordination and service quality.
7. Competitive Advantage
- Businesses can anticipate customer needs, adapt to trends, and stay ahead of competitors.
Customer Relationship Management is closely tied to several other business disciplines that enhance efficiency, customer satisfaction, and organizational success.
To understand how companies align people and performance with business goals, explore What Is Human Capital Management (HCM)? and What Is Talent Management?. Both explain how workforce strategies complement CRM initiatives by improving employee engagement and service delivery.
For businesses implementing CRM solutions during organizational changes, What is change management? and What Is Management Consulting? provide valuable insights into managing transformation effectively.
CRM systems often integrate with large-scale company projects — learn how these are structured in What Is Project Management? and What is agile project management?.
To understand how data supports personalized customer experiences, read How to Become a Data Scientist? and What Does a Data Engineer Do?
You can also see how similar principles of customer focus apply in other industries through What Is Hospitality Management? and What Is Sports Management?.
Challenges in CRM Implementation
Organizations may face the following challenges when adopting CRM:
- Resistance to Change – Employees may be hesitant to adopt new systems or processes.
- Data Quality Issues – Inaccurate or incomplete customer data undermines CRM effectiveness.
- Integration Difficulties – Connecting CRM with existing systems and tools can be complex.
- Cost of Implementation – Licensing, customization, training, and maintenance may require significant investment.
- Over-Reliance on Technology – Focusing solely on software without proper strategy and human engagement limits effectiveness.
- Complexity of Use – Poorly designed CRM systems may be difficult to navigate and reduce adoption rates.
CRM Metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Measuring CRM effectiveness is crucial to track success and ROI:
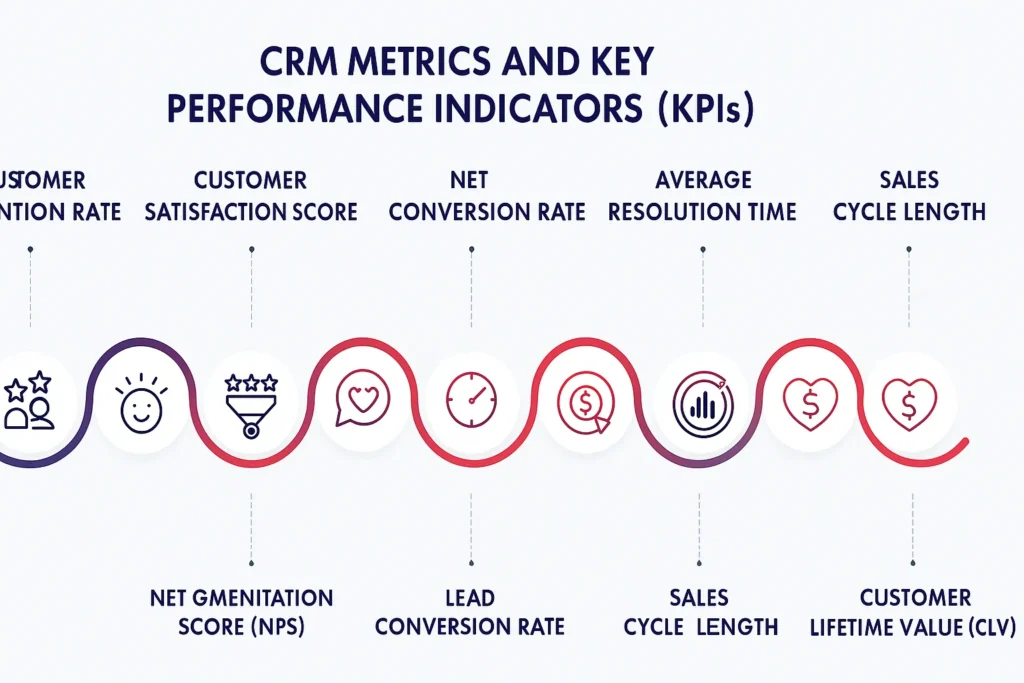
- Customer Retention Rate – Percentage of customers retained over a period.
- Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT) – Measures satisfaction with interactions and service.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS) – Assesses likelihood of customers recommending the company.
- Lead Conversion Rate – Percentage of leads converted into customers.
- Average Resolution Time – Time taken to resolve customer issues.
- Sales Cycle Length – Average time to close a deal.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) – Predicts total revenue generated from a customer over the relationship duration.
CRM Tools and Technologies
Modern CRM systems offer diverse features and capabilities:
- Salesforce – Cloud-based CRM for sales, marketing, and customer service.
- HubSpot CRM – Free and scalable CRM for small to large businesses.
- Zoho CRM – AI-powered CRM for sales, marketing, and analytics.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 – Integrated CRM and ERP platform.
- Oracle CX Cloud – Comprehensive customer experience and CRM solution.
- Freshsales – CRM focused on automation, analytics, and lead management.
Technologies supporting CRM include AI, machine learning, predictive analytics, cloud computing, mobile CRM, and social media integration.
Best Practices for Effective CRM
- Define Clear Objectives – Align CRM with business goals and customer experience strategies.
- Ensure Data Accuracy – Regularly clean and update customer data.
- Train Employees – Provide comprehensive training to ensure adoption and effective use.
- Customize CRM Systems – Tailor features and workflows to business needs.
- Integrate Across Departments – Share information between sales, marketing, and service teams.
- Monitor Performance – Use KPIs and analytics to track success and optimize strategies.
- Focus on Customer-Centric Culture – Encourage employees to prioritize customer needs in every interaction.
Real-World Applications of CRM
- Retail – Personalized promotions, loyalty programs, and inventory recommendations.
- Banking and Financial Services – Managing accounts, transactions, and customer inquiries.
- Healthcare – Patient relationship management, appointment scheduling, and follow-ups.
- E-Commerce – Managing online customer interactions, tracking orders, and resolving complaints.
- Hospitality – Reservation management, customer preferences tracking, and personalized services.
- Technology Companies – SaaS subscription management, support tickets, and upselling opportunities.
Future of CRM
CRM continues to evolve with advancements in technology and changes in customer expectations:
- AI-Powered CRM – Predictive analytics, intelligent recommendations, and automated insights.
- Omni-Channel Integration – Seamless customer experience across social media, email, chat, and in-person interactions.
- Voice and Chat Integration – AI chatbots and voice assistants enhance customer support.
- Hyper-Personalization – Tailoring experiences, offers, and communication based on real-time data.
- Mobile CRM – Access CRM on smartphones and tablets for remote and field teams.
- Customer-Centric Business Models – CRM as a core strategy for long-term loyalty and retention.
Conclusion
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is a critical strategy for building strong, lasting customer relationships while optimizing business operations. By integrating people, processes, and technology, CRM enables organizations to understand their customers better, provide personalized experiences, improve retention, and drive revenue growth.
Effective CRM implementation requires clear strategy, accurate data, employee training, and continuous monitoring. As businesses continue to embrace digital transformation, CRM will remain central to delivering exceptional customer experiences, maintaining competitive advantage, and fostering long-term success.
CRM is not just software—it is a philosophy, a strategy, and a set of practices that empowers organizations to put customers at the center of everything they do.


