
Executive Summary
In every organization, whether a small startup or a multinational corporation, management is the backbone that ensures goals are achieved efficiently and effectively. Management is the process of planning, organizing, leading, and controlling resources to achieve specific objectives.
This comprehensive guide explores what management is, its functions, principles, roles, types, benefits, challenges, and best practices, offering a detailed understanding for students, professionals, and business leaders.
Table of Content
Understanding Management
Management can be defined as the systematic process of coordinating human, financial, and physical resources to accomplish organizational objectives.
It involves:
- Setting objectives and goals
- Planning the steps to achieve them
- Organizing resources effectively
- Leading teams to implement plans
- Monitoring progress and making adjustments
Management is essential to transform resources into productive outcomes, ensuring the smooth functioning of organizations and other enterprises.
Why Management Matters
- Achieving Organizational Goals: Ensures that resources are used efficiently to meet objectives.
- Resource Optimization: Minimizes waste and maximizes output.
- Coordination and Collaboration: Aligns teams and departments for collective success.
- Adaptability: Helps organizations respond effectively to internal and external changes.
- Decision-Making Support: Provides a framework for evaluating options and taking actions.
- Motivation and Leadership: Guides employees to perform at their best.
Effective management is a key driver of productivity, growth, and sustainability in any organization.
Core Functions of Management
Management is traditionally categorized into five core functions, which provide a framework for effective organizational operation:
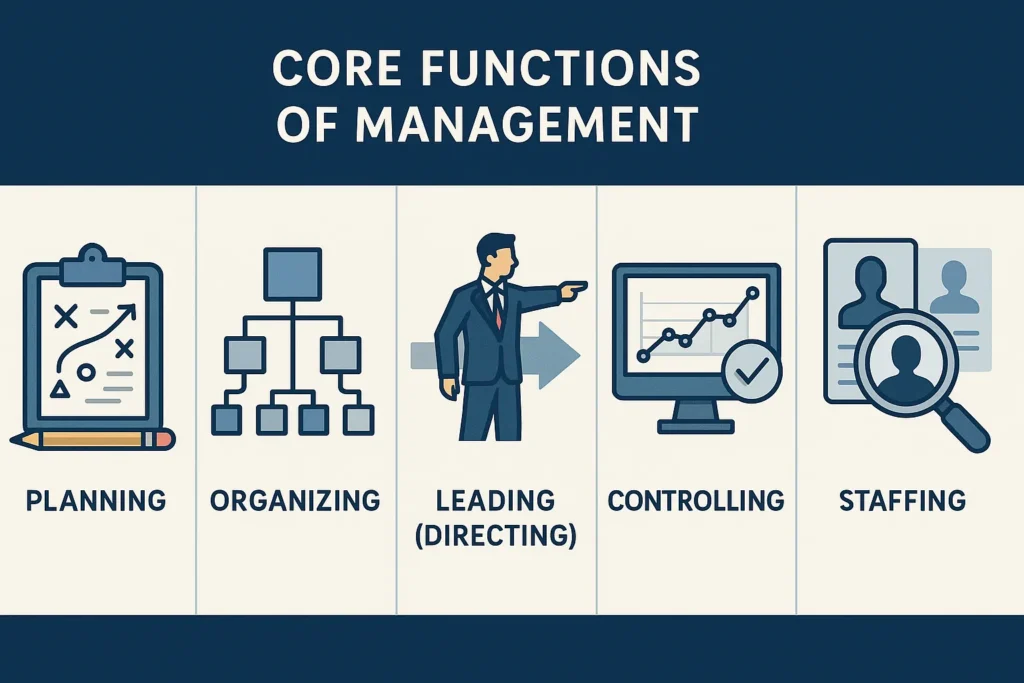
1. Planning
- Defining objectives and the actions required to achieve them.
- Forecasting future conditions and preparing strategies.
- Example: A company planning its annual sales targets and marketing strategy.
2. Organizing
- Arranging resources and tasks to implement plans.
- Establishing roles, responsibilities, and workflows.
- Example: Creating teams and assigning roles to ensure smooth project execution.
3. Leading (Directing)
- Guiding, motivating, and communicating with employees to achieve objectives.
- Fostering teamwork, culture, and engagement.
- Example: A manager providing feedback and encouragement to ensure high performance.
4. Controlling
- Monitoring performance and comparing it with goals.
- Implementing corrective actions when necessary.
- Example: Reviewing quarterly sales figures and adjusting strategies to meet targets.
5. Staffing
- Recruiting, training, and retaining the right talent.
- Ensuring the organization has the skills required to succeed.
- Example: Hiring specialized personnel for a new product development team.
Principles of Management
Several foundational principles guide effective management:
- Division of Work: Specialization increases efficiency and skill.
- Authority and Responsibility: Managers must have the right to give orders and be accountable.
- Discipline: Ensures adherence to rules and agreements.
- Unity of Command: Employees should receive instructions from one manager only.
- Unity of Direction: Teams should work towards the same objectives.
- Subordination of Individual Interest: Organizational goals take priority over personal interests.
- Remuneration: Fair compensation motivates employees.
- Centralization vs. Decentralization: Balance authority distribution for efficiency.
- Equity: Managers should be fair and just in their dealings.
- Order: Maintain proper placement of people and resources.
These principles, introduced by Henri Fayol, remain relevant in modern management practices.
Types of Management
Management can be categorized based on focus, scope, and function:
1. Strategic Management
- Focus on long-term objectives and corporate strategy.
- Example: Planning market expansion over five years.
2. Operational Management
- Day-to-day execution of tasks and processes.
- Example: Managing production schedules and quality control.
3. Financial Management
- Planning, organizing, and controlling financial resources.
- Example: Budgeting, investment decisions, and cost control.
4. Human Resource Management (HRM)
- Recruiting, training, and managing employees.
- Example: Implementing performance appraisal systems.
5. Marketing Management
- Planning and executing strategies to promote products and services.
- Example: Market research, pricing, and promotional campaigns.
6. Project Management
- Planning, executing, and closing projects effectively.
- Example: Launching a new software product within deadlines.
Related Reads to Explore
Expand your understanding of how management shapes business operations, people, and performance:
- What Is Business Management – Learn how organizations plan, organize, and control business functions effectively.
- What Is Operations Management – Discover how businesses manage daily processes to deliver products and services efficiently.
- What Is Performance Management – Understand how tracking and improving performance drives organizational growth.
- What Is Human Resource Management – See how HR plays a vital role in managing people and culture within organizations.
- What Is Management Consulting – Explore how consultants help companies improve operations, strategy, and performance.
- What Is Knowledge Management – Find out how organizations capture, share, and utilize information for better decision-making.
Skills Required for Effective Management
Successful managers possess a combination of technical, human, and conceptual skills:

- Leadership Skills: Inspire and guide teams effectively.
- Communication Skills: Clearly convey ideas, goals, and feedback.
- Decision-Making Skills: Analyze information and make informed choices.
- Problem-Solving Skills: Address challenges proactively and creatively.
- Time Management Skills: Prioritize tasks and meet deadlines.
- Analytical Skills: Interpret data for strategic planning.
- Negotiation Skills: Resolve conflicts and reach agreements beneficial to the organization.
A well-rounded manager balances people skills, business acumen, and technical expertise.
Recommended Courses to Enhance Your Management Skills
Take your management expertise to the next level with these top courses:
- Management Skills Certification Course (Now with AI!) – Learn modern management practices, enhanced with AI tools to improve decision-making and efficiency.
- Configuration Management and the Cloud – Understand how to manage systems, infrastructure, and cloud resources effectively.
- Introduction to Project Management – Build a solid foundation in planning, executing, and monitoring projects.
- Investment Risk Management Course – Gain insights into financial risk, portfolio management, and decision-making strategies.
- Engineering Project Management Specialization Course – Master managing complex engineering projects from planning to delivery.
Management Styles
Different situations require varying approaches to management:
- Autocratic Management: Manager makes decisions independently; quick but may demotivate staff.
- Democratic Management: Employees are involved in decision-making; boosts engagement but slower.
- Laissez-Faire Management: Hands-off approach; works well with highly skilled teams.
- Transactional Management: Focuses on structured tasks and rewards/punishments.
- Transformational Management: Inspires innovation, vision, and change.
The best management style depends on organizational culture, team dynamics, and specific goals.
Benefits of Effective Management
- Goal Achievement: Ensures that organizational objectives are met efficiently.
- Resource Optimization: Minimizes waste and maximizes productivity.
- Improved Employee Performance: Motivates and guides employees effectively.
- Adaptability and Resilience: Helps organizations navigate change and uncertainty.
- Better Decision-Making: Structured processes lead to informed choices.
- Enhanced Organizational Reputation: Reliable management fosters trust among stakeholders.
Management is a critical driver of organizational success, growth, and sustainability.
Challenges in Management
- Rapid technological changes and digital transformation
- Global competition and market fluctuations
- Cultural diversity and remote workforce management
- Balancing short-term performance with long-term strategy
- Managing limited resources and tight budgets
- Employee engagement and retention challenges
Addressing these challenges requires strategic planning, continuous learning, and adaptive leadership.
Real-World Examples of Management

- Apple Inc.: Strategic management focuses on innovation and premium product positioning.
- Toyota: Operational management ensures efficiency through lean manufacturing.
- Amazon: Project management drives rapid development and delivery systems.
- Google: Human resource management nurtures talent and fosters creativity.
- Unilever: Financial and marketing management maintain global growth and brand equity.
These examples show how effective management practices lead to success across industries.
Modern Trends in Management
- Digital Transformation: Leveraging AI, automation, and analytics in management processes.
- Remote and Hybrid Work: Managing distributed teams efficiently.
- Agile Management: Applying agile principles beyond IT to operations and strategy.
- Sustainable Management: Emphasizing environmental and social responsibility.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: Using real-time data for planning and execution.
Modern management combines traditional principles with technology, innovation, and adaptability.
Conclusion
Management is the art and science of coordinating resources, people, and processes to achieve organizational objectives. By understanding its functions, principles, skills, and best practices, individuals and organizations can maximize efficiency, productivity, and sustainability.
Whether you are leading a team, managing a project, or running a company, mastering management is essential for long-term success, growth, and innovation.


